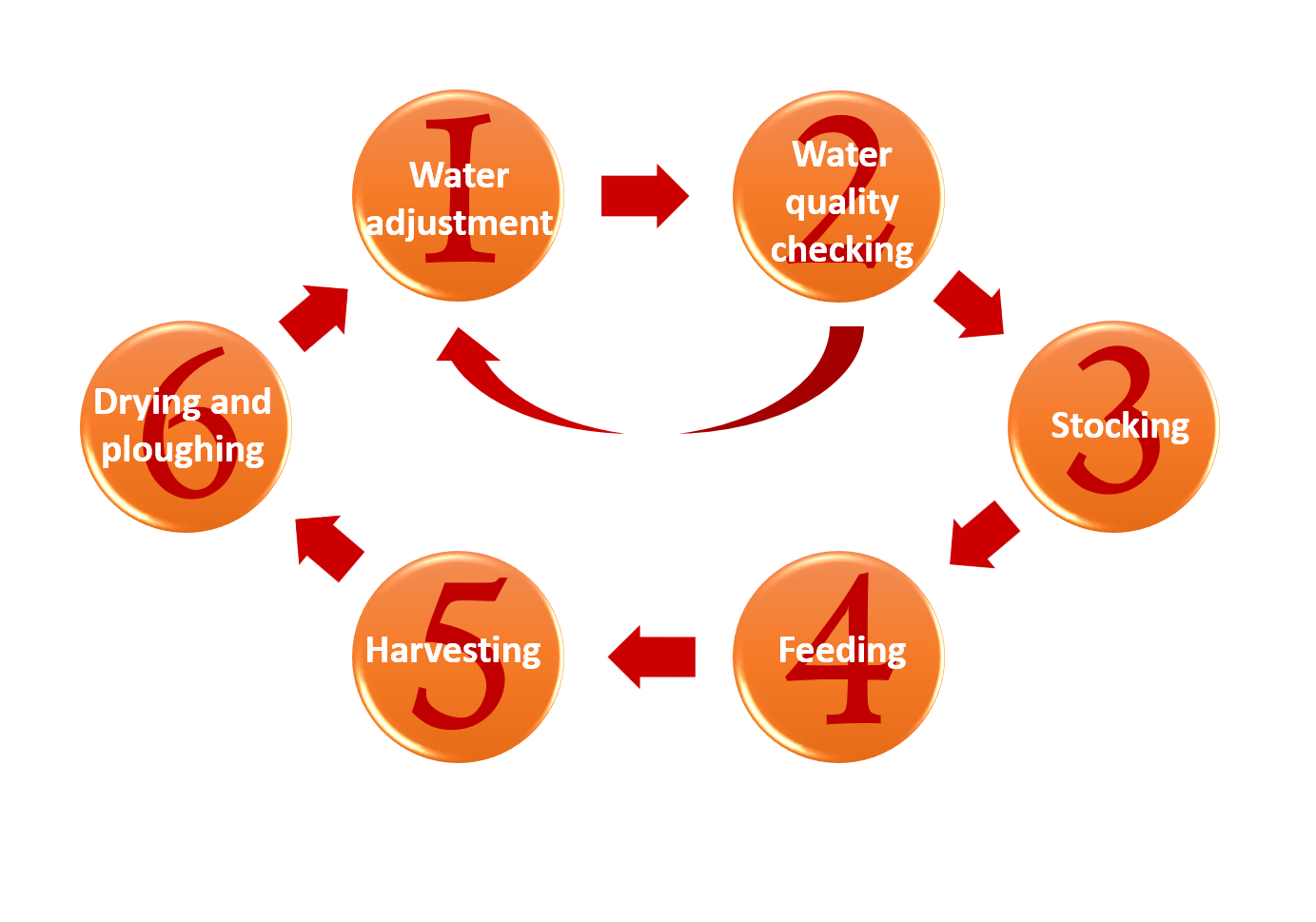
1. Water adjustment
After filling the pond with freshwater, Camellia seed powder is used to sterilize the pond. Lime is used to adjust the pH of the water. The pond is then fertilized with groundnut to cultivate planktons to feed the fish.
2. Water quality checking
A small number of fry or fingerlings are then added to check whether the water quality is good enough for them to survive.
3. Stocking
After checking that the fry can live normally, large number of fry or fingerlings is added into the pond. Most fry and fingerlings are imported from mainland China or Taiwan. Some grey mullet fry can be obtained from local coastal water.
4. Feeding
Depending on the variety and size of the fish, they will be fed with grass, bread, biscuits, soybean meal or artificial fish feed. The small fry use the planktons in the water and do not require feeding. Farmers may add natural or artificial fertilizers to promote the growth of planktons.
5. Harvesting
Although the fish farmers can take their harvest all year round, they often do so during the fishing moratorium or before festivals such as Lunar new year or Ching Ming festival. Harvesting is normally carried out at night and the caught is transported to the wholesale market for sale to retailers.
6. Drying and ploughing
Since harmful organisms accumulate at the bottom of the fishpond, the fish farmers often drain the ponds during the dry season. After the bottom soil is sun-dried, bulldozers are used to level the bottom and repair the pond bund to return the ponds to their original depth. Lime is added to adjust the pH of the soil. Normally, ponds are dried and ploughed every two to three years. Waterbirds will feed on the left-over small fish when the water level in the ponds decreases to low level.

Left: Wooden boat used by the fish farmers for feeding
Right: Modern feeding machine
As time passes, fish farmers develop different modes of pond fish culture. Depending on their personal ability, available capital, market supply and demand, and profit potential, the fish farmers adopt methods to manage the pond bunds, fish feed and water quality control that best suit their situation. The bunds may be formed from mud and covered with vegetation. Some bunds may be used to grow fruit trees. Some farmers may cover the bunds with man-made materials such as concrete or plastic sheet to prevent the growth of weeds. The fish feed may be bread, biscuits, soybean meal and instant noodles applied manually; or commercially formulated feed, sometimes with nutrient supplements, dosed with machine. In water quality control, some farmers judge the pH of the water by colour from experience. Others may use chemical analysis to determine the water quality.